Describe the Work Energy Theorem in Words and Equation
To investigate the validity of the work-energy theorem. This explanation can be extended to rigid bodies by describing the work of rotational kinetic energy and torque.

Energy Work Power 16 Of 31 Work Energy Principle An Explanation Youtube
The work-energy theorem states that the work you set right into a system is transformed into the vitality of the system.

. W is the total work done. The work-energy theorem also known as the principle of work and kinetic energy states that the total work done by the sum of all the forces acting on a particle is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of that particle. Which forces on m2 do no work.
ΔEk W net Ekf Eki 8000Δx0 0 139 445 8000Δx0 Δx0 139445 8000 174 m Δ E k W net E k f E k i 8000 Δ x 0 0 139 445. Δ KE of the bullet 12 002 500 2 002 400 2 Therefore Δ KE of the bullet 900 J. This idea is expressed in the following equation.
1 M2 Fsensor 2 Draw a free body diagram for each mass in this setup. M1 3 Considering all the forces acting on m write the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for. Substituting for axf - xo into our work equation we find that.
Wnet mvf2 - mvo2. 1 Describe the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem in words and summarize with an equation. W K mv 2 2 2 - mv 1 2 1 Equation 1 is a.
Energy is part of essential theories in science. 305 words 2 page s The primary objective of this lab is to verify the generalized work-energy theorem. Force applied to an object changes the motion of an object.
See the answer See the answer done loading. Hence using the Work-Energy Theorem we have. K i initial kinetic energy.
Start your trial now. Also explain that we buy electricity in kilowatt-hours because when power is multiplied by time the time units cancel which leaves work or energy. 4 which forces on m2 do no work.
W 1 2 m v f 2 1 2 m v i 2. 3 considerinf all the forces acting on m2 write the work kinetic energy theorem for m2. The Work-Energy principle depicts that the rise in the Kinetic-Energy of a rigid body is because of the ve Work done on the body by the net resultant force that acts on it.
Chance to take on the big one. Final velocity of the bullet 400 ms. First week only 499.
W n e t Δ K K f K i. The work W done by the net force on a particle equals the change in the particles kinetic energy K E. This problem has been solved.
This equation is one form of the work-energy equation and gives us a direct relation between the net work done on a particle and that particles velocity. The quantity 1 2mv2 1 2 m v 2 in the work-energy theorem is defined to be the translational kinetic energy KE of a mass m moving at a speed v. So according to the theorem statement we can define the work-energy theorem as follows.
W Net-work done on the object. Translational kinetic energy is distinct from rotational kinetic energy which is considered later In equation form the translational kinetic energy KE 1 2mv2 KE 1 2 m v 2 is the energy. 2 draw a free body diagram for each mass in this setup.
Where W is the work done by object measured using Joules. In physics we take measurable quantities from the real world and attempt to find meaningful relationships between them. Describe the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem in words and summarize with an equation.
Apply the work-enemy theorem. Where K f Final kinetic energy. Work transfers energy from one place to another or one form to another.
The work-energy theorem affirms that the work done on any object is comparable to the difference in kinetic energy of the object. The work-energy theorem can be derived from Newtons second law. K f K i W.
Work and energy are directly proportional to each other. W N work done by a normal force. According to Work energy theorem Work done by all the forces Change in Kinetic Energy.
W K2 K1 ΔK 3 3 W K 2 K 1 Δ K. The change in kinetic energy is equal to the work done. 1 describe work kinetic energy theorem in words and summarize with an equation.
Now if we can calculate the change in energy of the bullet or in other words the workdone by the bullet on the tree we have. A basic example of this would be the physical ideal of force. Δ K is the change in kinetic energy.
The Equation 3 3 is also called work-energy theorem and in this case the work is equal to the change in kinetic energy so we call it work-kinetic energy theorem. M1 3 Considering all the forces acting on m write the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for. If W f d W f d and work can be expressed in J then P W t f d t P W t f d t so power can be expressed in units of N m s N m s.
If an amount of work W is done on a system then the kinetic energy K of the system changes. In this lab we shall also look at the Newton Second Law a little bit laying more emphasis on the energy that is involved. Mathematically E W.
W g W N W f K f K i. After the net force is removed no more work is being done the objects total energy is altered as a result of the work that was done. The Work-Energy Theorem - Ximera.
Solution for State the Work-Energy theoremequation words and equations. The work-energy theorem also known as the principle of work and kinetic energy states that the total work done by the sum of all the forces acting on a particle is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of that particle. M is the mass of the object measured using kilograms.
Substitution is given a physical meaning. K i Initial kinetic energy. The change in the kinetic energy is equal to the amount of work done.
Work done by an object can be mathematically expressed as. W f work done by friction. Wnet ma xf - xo Given uniform acceleration vf2 - vI2 2axf - xo.
The place W is the work and E is the change of vitality because of the work. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for. K f final kinetic energy.
From the study of the numerous forms of energy. M2 Fsenson 2 Draw a free body diagram for each mass in this setup. A constant force will produce constant acceleration.
Conversely a decrease in Kinetic Energy is caused by the negative Work done by. Where W g work done by gravity. Types of Work-Energy Theorem.
W ΔKE 1 2mv2 f 1 2mv2 i W Δ KE 1 2 mv f 2 1 2 mv i 2. Work done by a constant force.
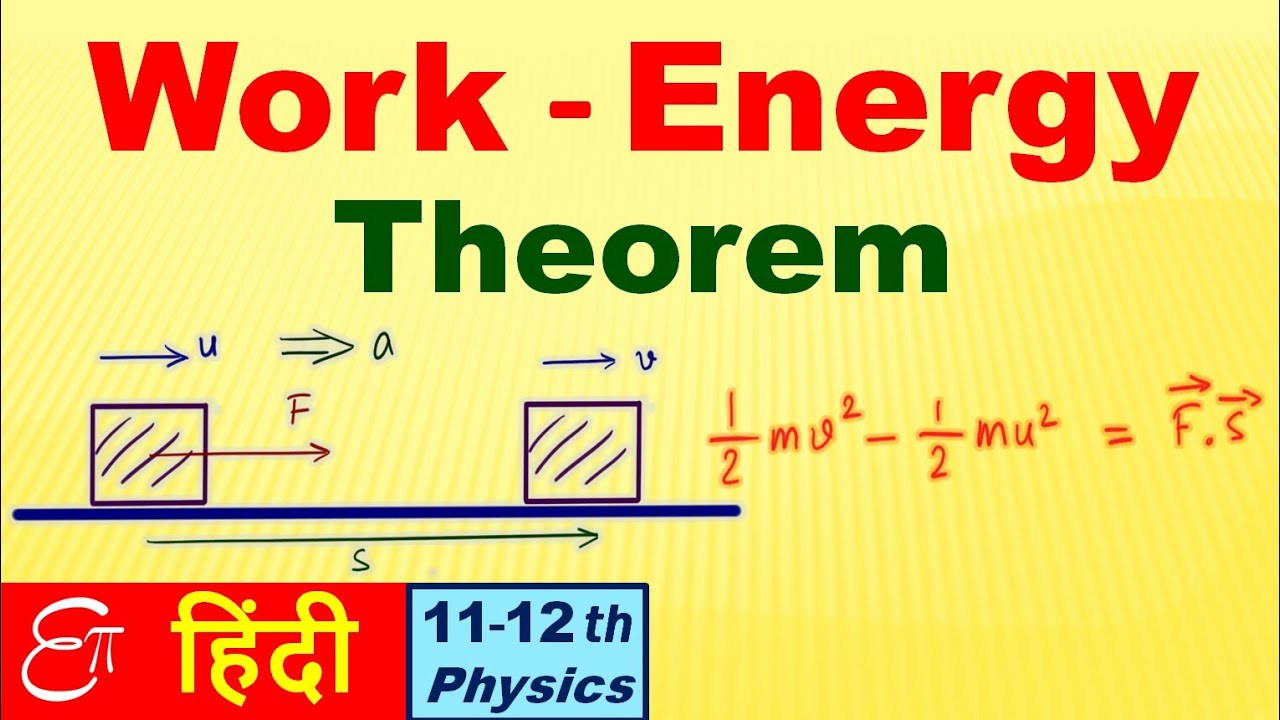
Work Energy Theorem Work Energy Power 2 In Hindi Youtube
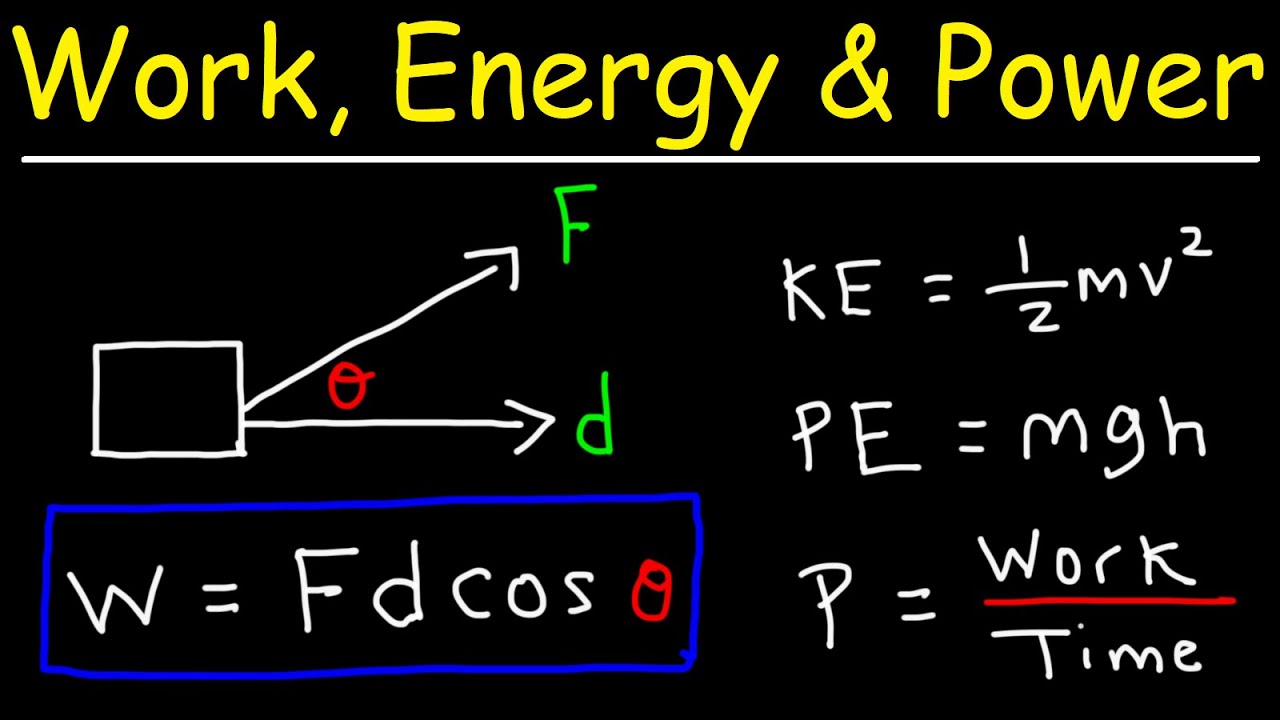
Work Energy And Power Basic Introduction Youtube

Work Energy Theorem Review Article Khan Academy

The Work Energy Theorem Objectives Investigate Quantities Using The Work Energy Theorem In Various Situations Calculate Quantities Using The Work Energy Ppt Download
No comments for "Describe the Work Energy Theorem in Words and Equation"
Post a Comment