Explain in General How Fluorescence Differs From Absorbance Spectrophotometry
Explain how this differs in fluorescence spectroscopy. 2 Φ emitted photons absorbed photons.
Fluorescence Spectroscopy Jasco
In fluorescence spectroscopy you use a given wavelength of light to excite a molecule and then monitor for fluorescence at a longer wavelength note the excitation and emission wavelengths are unique for the molecule.

. Absorbance A logP0P Beers Law View the full answer Transcribed image text. The key difference between absorbance and fluorescence is that we can use an absorbance analysis technique to directly measure the amount of a specific wavelength that is absorbed by a sample without dilution or assay preparation whereas fluorescence analysis requires sample preparation in which sample of interest must be bound with the fluorescent. In absorbance spectroscopy some light is absorbed by the sample and the light not absorbed is detected.
In the absorption spectrum and frequently the emission spectrum will be approximate to a mirror image of the absorption spectrum. Explain the difference between an absorbance and fluorescence excitation and emission spectra. In some materials.
Difference Between Fluorescence and Luminescence Mechanism. It involves using a beam of light usually ultraviolet light that excites the electrons in molecules of certain compounds and causes them to emit light. Fluorescence and phosphorescence come at lower energy than absorption the excitation energy.
So the more light that is absorbed the higher the concentration of the compound in the sample. An excited singlet state is produced in the. They have different sample size.
4 x 10-6 x 1 k 59545 mol dm-3 cm-3. Absorbance k c t k absorbance c t k 0. Fluorescence microscopy measures the fluorescence of a particular compound.
Therefore k the molar extinction coefficient is 59545 mol dm-3 cm-3. A wavelength scan whether performed all at once using a multi-element ccd or sequentially by moving a prism or diffraction grating is generally made with a. UV-vis absorption spectroscopy probes transitions between electronic states in a material.
Whereas measuring absorbance requires measuring the slight dimming of a bright light fluorescence spectroscopy looks for light that is produced directly by the sample. In other words fluorescence is measured over a dark background while absorbance is measured over a bright background. Since the emission of fluorescence always takes place from the lowest vibrational level of the first excited state the shape of the emission spectrum is always the same despite changing the wavelength of exciting light.
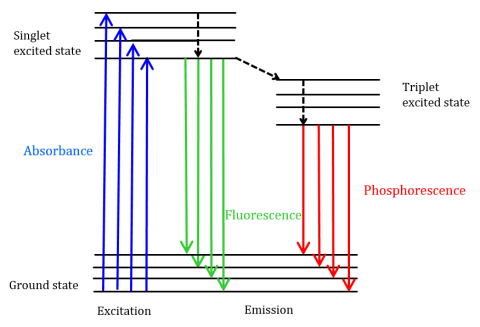
There are various definitions of fluorescence and phosphorescence with the simplest being that fluorescence is prompt photoluminescence that occurs very shortly after photoexcitation of a substance while phosphorescence is long-lived photoluminescence that continues long after the photoexcitation has ceased. Luminescence refers to any mechanism where photons are generated without an input of heat. The absorption of a photon of energy by a fluorophore which occurs due to an interaction of the oscillating electric field vector of the light wave with charges electrons in the molecule is an all or none phenomenon and can only occur with incident light of specific wavelengths known as absorption bands.
One major difference between the two methods is the light detector in absorbance spectroscopy is in line with the light path and the. An indication of the potential sensitivity of fluorometry is that the search for single-molecule detection has been based almost exclusively on the use of fluorescent compounds. As shown in Figure in absorption wavelength λ 0 corresponds to a transition from the ground vibrational level of S 0 to the lowest vibrational level of S 1.
A complementary technique is absorption spectroscopy. Fluorescence refers to a specific type of luminescence where the energy to produce the photon comes from the absorption of a photon with higher energy. Fluorescence spectroscopy is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
Typically but not necessarily visible light. A spectrophotometer is a spectrometer that measures light intensity key term-photometer at some wavelength s. Absorbance is measured as the difference in intensity between light passing through the reference and the sample whereas fluorescence is measured directly without any reference beam.
On the other hand the spectrophotometer measures the samples transmittance or reflectance of color as a function of wavelength. They differ in range. Its usually used to measure the concentration of a compound in a sample.
Support the following claim about a difference between a spec20 and a plate reader. They differ greatly in functions. While this is a simple definition it does not explain why such a.
If the absorbed photon contains more energy than is. The maximum fluorescence quantum yield is 10 and compounds with quantum yields of 010 are still considered fluorescent. It is the ratio of photons emitted to photons absorbed.
If every photon absorbed results in a photon emitted. It is possible to measure fluorescence much more sensitively than absorbance. We can find the molar extinction coefficient by substituting values of absorbance and the concentration of the unknown concentration of methylene blue into Beers laws equation.
Absorbance spectroscopy measures how much of a particular wavelength of light gets absorbed by a sample. In contrast absorption spectrophotometry requires measurement of transmitted light relative to high incident light levels at the same wavelength. Answered 5 years ago.
A colorimeter is designed to measure the absorption ability of a particular color in a given sample. A spectrometer is an instrument that measures properties of light. Fluorometry was introduced in immunological assays to improve immunoassay sensitivity.
A complementary technique is absorption spectroscopy. FTIR is an absorption spectroscopy - or reflection depending on the geometry. Fluorescence spectroscopy also known as fluorometry or spectrofluorometry is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample.
It is relatively easy to detect low levels of. Fluorescence and phosphorescence are photon emission processes that occur during molecular relaxation from electronic excited states. Relation between Absorption and Emission Spectra.
In general the sensitivity of fluorescence is 101000-fold higher in comparison to absorbance measurements. Fluorescence Spectra The entire fluorescence process is cyclical.
Fluorescence Spectroscopy Jasco

Uv Vis Absorption Spectrum Of 10 M M Fluorescein In Water Medium With Download Scientific Diagram

Absorbance Detection Surgical Instruments Research Instruments Laboratory Equipment Wpi

No comments for "Explain in General How Fluorescence Differs From Absorbance Spectrophotometry"
Post a Comment